
TDS Return File: Know How to File TDS/TCS Return, the Due Dates of e-Filling TDS/TCS in the FY 2021-22, Late Filing Fee, and More
March 11, 2021
Understand The Basic Concepts Of E-Invoices In Detail
March 17, 2021What is E-Invoice?
As per exiting law, every supplier of Goods or services is required to issue taxable invoice to the recipient/buyer manually or through ERP system.
Under E-Invoice, this system of invoicing has been digitalized and routed through the centralized government portal for notified class of registered persons.
That does not mean that invoice needs to be generated through government portal. In fact, invoice will be generated through the existing ERP system used by the taxpayer, with the only requirement being, the software’s ability to generate the invoice in the given e-invoice limit standard format and parameters (as per FORM GST INV-01) which is being validated on real-time basis through centrally organized government system (Invoice Registration Number (IRN) portal).
To give effect to this new provision, Sub-Rules (4), (5) and (6) has been added under rule 48 of the existing CGST Rules through notification number 68/2019 – Central Tax.
Purpose of E-Invoice:
Through e-invoice generation system government is aiming to curb the Tax evasion and ease the compliance burden on tax payer. {E.g.: Automation of generation of E-way Bill, Filling of period Tax Returns, Reconciliation of Input tax Credit etc.}
Who is required to issue E-Invoice?
With effect from 1st day of October, 2020, E-Invoicing is applicable on every registered, whose aggregate turnover exceeds 500 crores in any financial year (FY) since 2017-18 for all its B2B and export transactions. {Notification 70/2020 – Central Tax read with Notification 70/2019, 13/2020, 61/2020 – Central Tax}.
Further, w.e.f. 1st day of January 2021, E-Invoicing extended to every registered person with aggregate turnover of exceeding 100 crores. {Notification 88/2020 – Central Tax}.
E.g.: ABC Ltd. Has aggregate turnover of 90 crores during FY 2017-18 and 110 crores during FY 2018-19 and 100 crores during FY 2019-20, then E-Invoicing is applicable as aggregate turnover for FY 2018-19 exceeds the limit of 100 crore.
Persons exempt from E-Invoicing:
Following persons are exempt from E-Invoicing:
- A special Economic Zone Unit {Notification No. 61/2020 – Central Tax}
- Special persons as per Rule 54 {Notification No. 13/2020 – Central Tax}
(i) Sub-Rule (2) – Insurer or a banking company or a financial institution, including a non-banking financial company;
(ii) Sub-Rule (3) – Goods transport agency supplying services in relation to transportation of goods by road;
(iii) Sub-Rule (4) – Supplier of passenger transportation services;
(iv) Sub-Rule (4A) – Person supplying services of exhibition of cinematograph films in multiplex screens.
Benefits of E-Invoice system:
- Real-Time Reporting: Real-time reporting will result into faster availability of input tax credit of the recipient and faster resolution of disputes.
- Curbing Tax Evasion: E-Invoicing will curb the practice of tax evasion as invoices will be generated and authenticated in real time. Thus, subsequent alternation after completion of transaction / Delivery of goods will not be possible.
- Standardization of Invoices: As invoices will be generated in required standard format with set parameters. It will be bringing practice of standardization of invoicing throughout the country which will help in interoperability.
- Reduction in duplicity of data: Data provided in E-Invoicing will be used to auto-populated other documents generation. Thus, it will help in reduction of duplicity and mismatch of data.
- Reduction of compliance burden: Compliance requirements will be relaxed due to common repository being used for other compliances like E-Way bill generation, Periodic tax fillings etc.
Disadvantages of E-Invoice system:
- Non-Reporting of B2C Transactions: Currently only B2B transactions are covered under E-invoicing requirement and not the B2C transactions. Thus, this system is not able to give holistic view of transactions entered and 100 percent automation.
- Non-Tracing of ITC in case of B2C Transactions: Maximum number of frauds happen in B2C invoices where question of availment of ITC is not involved hence the basic purpose or advantage of E-invoicing will be fulfilled only after complete implementation for all types of invoicing.
- Data Security: Organizations will be required to upload each and every invoice at GSTN portal which may increase risk to data security and chances of hacking of confidential information of the entity.
Process of E-Invoice Generation:
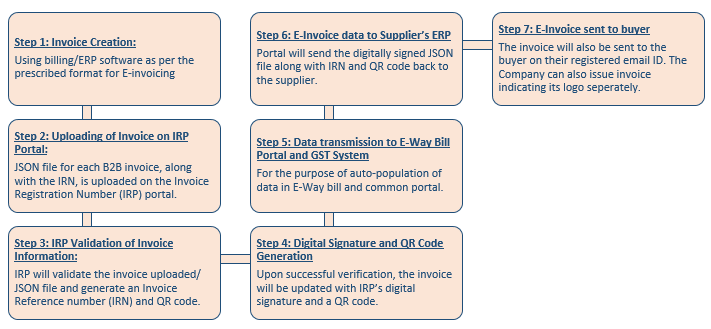
Documents required to be generated through E-Invoice system:
- Taxable Invoice (B2B)
- Credit Notes
- Debit Notes
- Other Documents Specified (No documents specified yet)
Documents not required to be generated through E-Invoice system:
- Taxable Invoice (B2C)
- Delivery Challan
- Bill of supply
- Jobs work challan
Structure of Invoice Reference number (IRN)
IRN Number will consist the following information:
- GSTN of supplier (E.g.: 01AAAAA1111A19Z)
- Financial Year (E.g.: 2019-20)
- Document Type – INV/CRN/DBN
- Document Number (E.g.: AA01234)
Basis above information, system will generate a 64-digit alphanumeric IRN number based on hashing string
(E.g.: 23f498ee41441ecad30f72ba5b9907506c3df70a17b0e0dff46b76a786400662)
Invoice Registration Number (IRP) portal: {Notification No. 69/2019}
Government has notified 10 IRP portals for generation of E-Invoice. One may think why 10 different portals has been notified for single purpose. All these portals are replica of each other and doesn’t make any difference. Various portal provided only to reduce traffic/ burden on single site and one can use any portal for the purpose of E-Invoicing.
Amendment/cancellation of E-Invoice:
The cancellation request can be triggered within 24 hours from the time of reporting invoice to IRP but can’t be amended. Amendment can be done during filling of GSTR-1. However, these changes will be flagged to proper officer for information.
Non-compliance of E-invoice norms:
Every person who is required to issue E-invoice must issue the invoice in manner specified. If supplier is failed to do so the Invoice issued shall not be treated as invoice {Rule 48(5) of CGST Rules}
Thus, the invoice issued will not be a legal document and void-ab-initio. Consequently, supplier will become non-compliant of invoicing norms and penalties or late fee may follow. Further, the buyer will not be able to avail ITC on goods or services procured.
Way Forward:
- On 8th March 2021, the CBIC notified that e-Invoicing will be applicable from 1st April 2021 for businesses with a turnover of more than Rs.50 crores (in any financial year from FY 2017-18 onwards, as intimated in Notification No. 5/2021 – Central Tax.
- Operating hurdles in implementation of E-Invoice system: Most of the business entities are not technologically upgraded to handle this noble E-invoicing system. And There may also be traffic issue site crash of GST Network to handle big check of data. These operating hurdles should be effectively taken care off.

Try HostBooks
SuperApp Today
Create a free account to get access and start
creating something amazing right now!
















